CAPSULES:
Capsules are solid dosage forms in which medicinal agents are enclosed within hard or soft soluble shell of gelatin.
The capsules are regarded as container drug delivery system that provides a tasteless/odorless dosage form without need for secondary coating step.
Advantages of Capsules:
- Tasteless and Odorless
- Swallowing is easy
- Aesthetically pleasant
- Convenient to carry
- Easy to store and dispense
- Easy to identify
- Dose accuracy
- Flexibility in formulating
Disadvantages of Capsules:
- Tend to be more expensive to produce than Tablets
- Not suitable for highly hygroscopic material
- The requirement for specialized manufacturing equipment
- Potential stability problems associated with capsules containing liquid fills
- Problems regarding the homogeneity of fill weight and content may be associated with capsule formulations
TYPES OF CAPSULES:
Capsules can be broadly classified into two types depending upon the nature of shell.
- Hard Gelatin Capsules
- Soft Gelatin Capsules
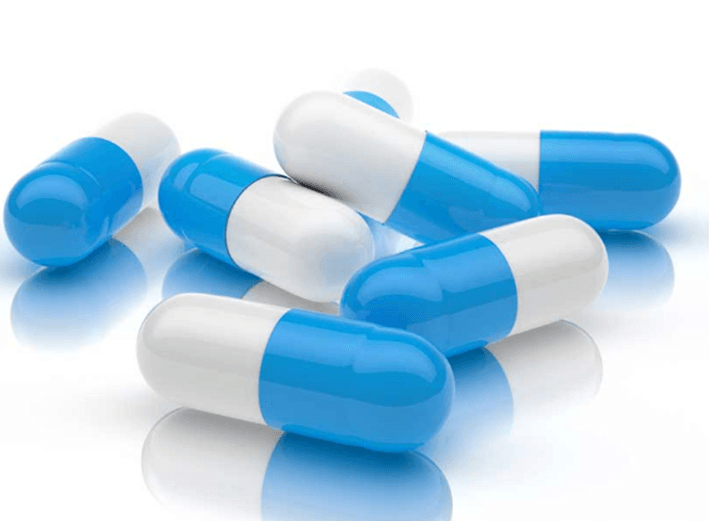
HARD GELATIN CAPSULES:
- Hard gelatin capsules are composed of two halves, termed as the ‘cap’ and the ‘body’.
- During manufacture of the dosage form, the formulation is filled into the body (using a range of different mechanical techniques) and the cap is pushed into place.
- The two halves of the capsule are joined, the cap overlapping with the body.
- Due to the tight fit between the two halves, separation of the cap and body does not normally occur under normal storage conditions or in clinical use.
These are normally used for dry, powdered ingredients, pellets or Tablets.
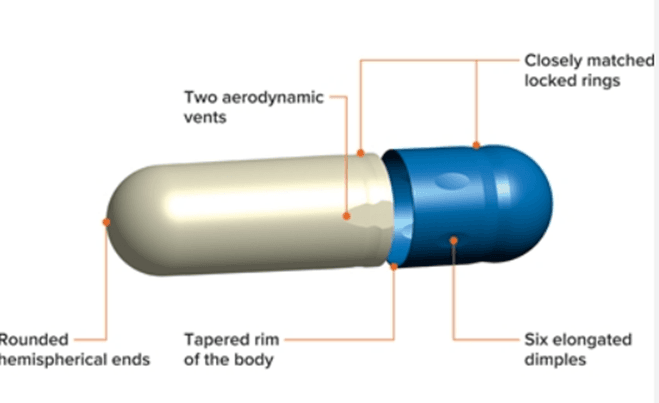
CAPSULE SIZES:
- Size depends on the amount of fill material to be encapsulated and the density / compressibility of the fill.
- The sizes of empty capsules:
- For human use: 000(the largest), 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (the smallest).
- For veterinary use: larger capsules are available.
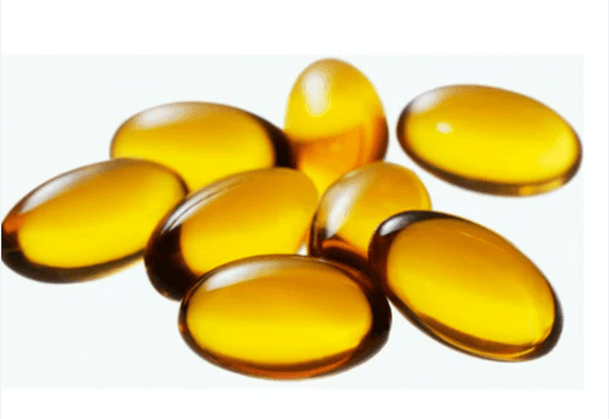
SOFT GELATIN CAPSULES (SOFTGELS):
- Consist of a continuous gelatin shell surrounding a liquid core
- Formed, filled, and sealed in one operation
- Shells are softened by addition of glycerine or polyhydric alcohol (ex. sorbitol)
- Oblong, spherical, elliptical in shape
- Primarily used for pastes / oils and for active ingredients that are dissolved or suspended in oil

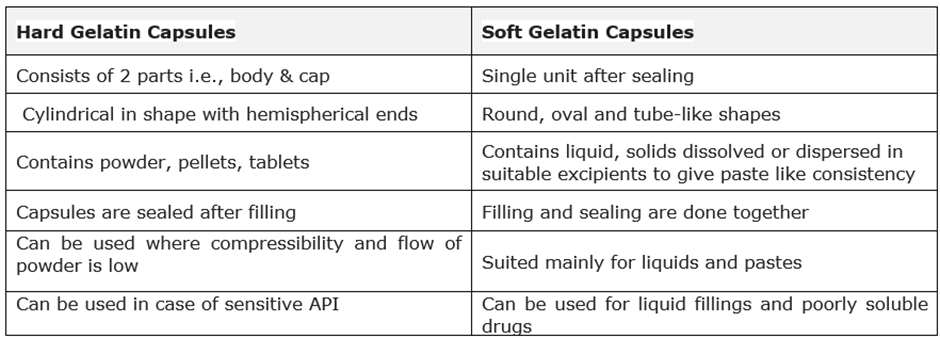
Comparison of Hard gelatin and soft gelatin capsules:
Basic components of Capsules:
- Gelatin Blend
- Drug (powder, pellets or Tablets)
- Diluents / Fillers
- Glidants
- Disintegrants
Gelatin Blend:
Gelatin is of two types
- Type A Gelatin
- Type B Gelatin
Type A Gelatin:
Derived from an acid-treated precursor and exhibits an isoelectric point in the region of pH 9. It is produced by hydrolysis and manufactured mainly from pork skin.
Type B Gelatin: Produced by alkaline hydrolysis, it is manufactured mainly from animal bones. Bone gelatin contributes firmness, whereas pork skin gelatin contributes plasticity, clarity.