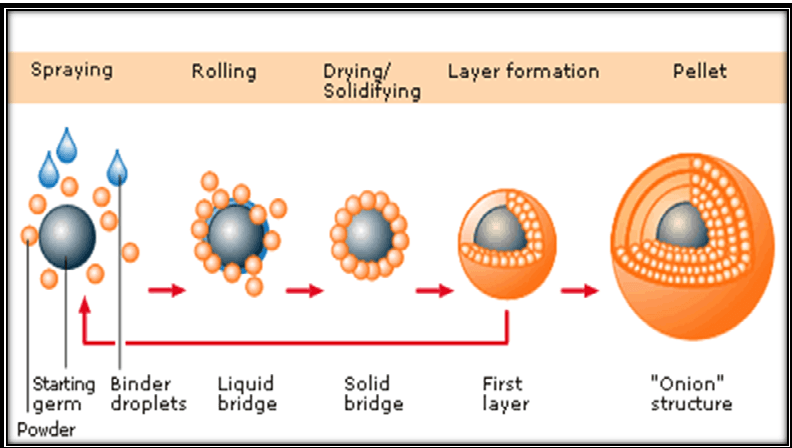
This method entails the application of successive layers of drug powder, along with excipients or both, onto pre-formed nuclei or cores using a binding liquid. During the powder layering process, the binding solution and finely milled powder are introduced simultaneously to a bed of starter seeds at a predetermined controlled rate.
In the initial phases, the drug particles adhere to the starter seeds and subsequently to the forming pellets through liquid bridges created by the sprayed binding liquid. These liquid bridges are eventually replaced by solid bridges formed either from a binder present in the liquid medium or from other materials. The successive layering of the drug and binder solution continues until the desired pellet size is achieved.
The initial equipment employed for the commercial production of pellets was the traditional coating pan; however, it has notable limitations, particularly regarding its inadequate mixing efficiency and ineffective drying process. During these operations, it is crucial to ensure that the powder is delivered precisely at a specified rate. If the balance between the binder liquid application rate and the powder delivery rate is not upheld, issues such as over-wetting or dust generation may arise, ultimately hindering both the quality and yield of the final product.
Furthermore, fines can arise from the friction between inner particles and the wall, which may manifest in the yield. This issue can be addressed by spraying the application medium onto the cascading pellets at the end, thereby enhancing the moisture content on the surface of the pellets and promoting the layering of fines onto them. To achieve this, equipment such as tangential spray granulators and centrifugal bed granulators are currently utilized.
