Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms:
Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered to sites of action within the body.
The requirement for dosage forms:
- Accurate dose.
- Protection ex: coated Tablets, sealed ampoules.
- Protection from gastric juice.
- Masking Taste and Odour.
- Placement of drugs within body tissues.
- Sustained release medication.
- Controlled release medication.
- Optimal drug action.
- Insertion of drugs into body cavities (rectal, vaginal)
- Use of desired vehicle for insoluble drugs.
Classification of pharmaceutical dosage forms:
Dosage forms are classified according to route of administration and physical forms.
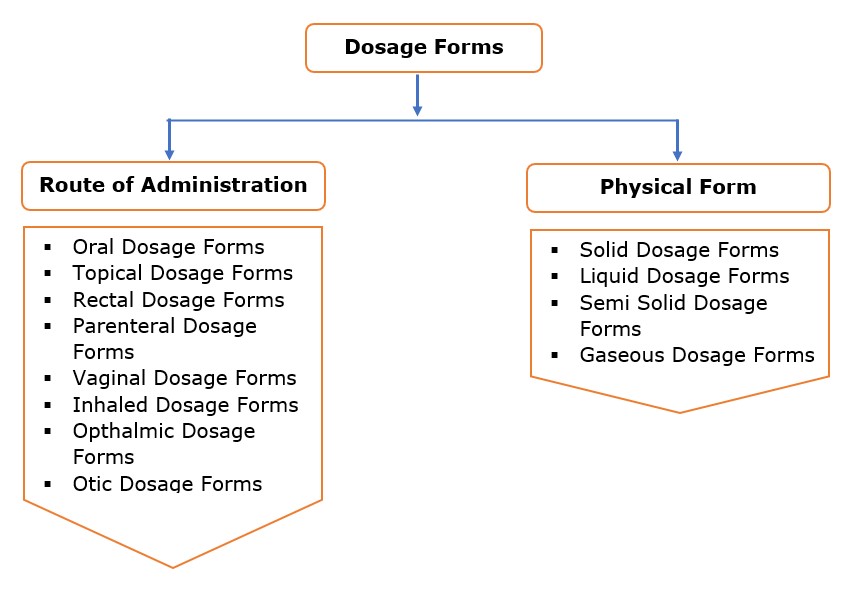
ORAL DOSAGE FORMS:
SOLID DOSAGE FORMS
TABLET: A tablet is a hard, compressed medication in round, oval or square shape.
A coating may be applied to:
- hide the taste of the tablet’s components.
- make the tablet smoother and easier to swallow .
- make it more resistant to the environment.
- extending its shelf life.

BUCCAL AND SUBLINGUAL TABLET:
- Sublingual and buccal medications are administered by placing them in the mouth, either under the tongue (sublingual) or between the gum and the cheek (buccal).
- The medications dissolve rapidly and are absorbed through the mucous membranes of the mouth, where they enter into the bloodstream.
- Avoid the acid and enzymatic environment of the stomach and the drug metabolizing enzymes of the liver.
- Examples of drugs administered by this route: e.g. vasodilators, steroidal hormones.
EFFERVESCENT TABLET:
- Effervescent Tablets are uncoated tablets that generally contain acid substances (citric and tartaric acids) and carbonates or bicarbonates and which react rapidly in the presence of water by releasing carbon dioxide.
- These Tablets are intended to be dissolved or dispersed in water before use providing:
- Very rapid tablet dispersion and dissolution.
- pleasant tasting carbonated drink.

CHEWABLE TABLET:
- Tablets that chewed prior to swallowing.
- They are designed for administration to children e.g. vitamin products.

CAPSULE: A capsule is a medication in a gelatine container.
The two main types of capsules are:
hard-shelled capsules, which are normally used for dry, powdered ingredients
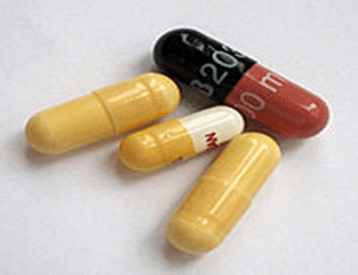
soft-shelled capsules, primarily used for oils and for active ingredients that are dissolved or suspended in oil.

LOZENGE:
- It is a solid preparation consisting of sugar and gum, the latter giving strength and cohesiveness to the lozenge and facilitating slow release of the medicament.
- It is used to medicate the mouth and throat for the slow administration of indigestion or cough remedies.

POWDER (ORAL):
There are two kinds of powder intended for internal use.
- Bulk Powders are multidose preparations consisting of solid, loose, dry particles of varying degrees of fineness. They contain one or more active ingredients, with or without excipients and, if necessary, coloring matter and flavoring substances.
- Divided Powders are single-dose presentations of powder (for example, a small sachet) that are intended to be issued to the patient as such, to be taken in or with water.
LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS:
ORAL SOLUTIONS:
Oral solutions are clear Liquid preparations for oral use containing one or more active.
ingredients dissolved in a suitable vehicle.

ORAL EMULSIONS:
Oral emulsions are stabilized oil-in-water dispersions, either or both phases of which may contain dissolved solids.

ORAL SUSPENSIONS:
- Oral suspensions are Liquid preparations for oral use containing one or more active ingredients suspended in a suitable vehicle.
- Oral suspensions may show a sediment which is readily dispersed on shaking to give a uniform suspension which remains sufficiently stable to enable the correct dose to be delivered

SYRUP:
- It is a concentrated aqueous solution of a sugar, usually sucrose.
- Flavoured syrups are a convenient form of masking disagreeable Tastes.

ELIXIR:
- It is pleasantly flavored clear liquid oral preparation of potent or nauseous drugs.
- The vehicle may contain a high proportion of ethanol or sucrose together with antimicrobial preservatives which confers the stability of the preparation.

LINCTUSES:
- Linctuses are viscous, liquid oral preparations that are usually prescribed for the relief of cough.
- They usually contain a high proportion of syrup and glycerol which have a demulcent effect on the membranes of the throat.
- The dose volume is small (5ml) and, to prolong the demulcent action, they should be taken un-diluted
ORAL DROPS:
Oral drops are Liquid preparations for oral use that are intended to be administered in small volumes with the aid of a suitable measuring device. They may be solutions, suspensions or emulsions.
GARGLES:
- They are aqueous solutions used in the prevention or treatment of throat infections.
- Usually, they are prepared in a concentrated solution with directions for the patient to dilute with warm water before use
MOUTHWASHES:
These are similar to gargles but are used for oral hygiene and to treat infections of the mouth.
TOPICAL DOSAGE FORMS:
OINTMENTS:
- Ointments are semi-solid, greasy preparations for application to the skin, rectum or nasal mucosa.
- The base is usually anhydrous and immiscible with skin secretions. – Ointments may be used as emollients or to apply suspended or dissolved medicaments to the skin
CREAMS:
Creams are semi-solid emulsions that are mixtures of oil and water.

They are divided into two types:
- Oil-in-water (O/W) creams: which are composed of small droplets of oil dispersed in a continuous aqueous phase. Oil-in-water creams are more comfortable and cosmetically acceptable as they are less greasy and more easily washed off using water.
- Water-in-oil (W/O) creams: which are composed of small droplets of water dispersed in a continuous oily phase. Water-in-oil creams are more difficult to handle but many drugs which are incorporated into creams are hydrophobic and will be released more readily from a water-in-oil cream than an oil-in-water cream. Water-in-oil creams are also more moisturizing as they provide an oily barrier which reduces water loss from the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin.
RECTAL DOSAGE FORMS:
SUPPOSITORY:
It is a small solid medicated mass, usually cone-shaped, that is inserted either into the rectum (rectal suppository), vagina (vaginal suppository or pessaries) where it melts at body temperature.

VAGINAL DOSAGE FORMS:
PESSARIES
- Pessaries are solid medicated preparations designed for insertion into the vagina where they melt or dissolve.
There are three types:
- Moulded pessaries: they are cone shaped and prepared in a similar way to moulded suppositories.
- Compressed pessaries: made in a variety of shapes and are prepared by compression in a similar manner to oral tablets.
- Vaginal capsules: are similar to soft gelatine oral Capsules differing only in size and shape.
PARENTERAL DOSAGE FORMS:
An injection is an infusion method of putting liquid into the body, usually with a hollow needle and a syringe which is pierced through the skin to a sufficient depth for the material to be forced into the body.
INHALED DOSAGE FORMS:
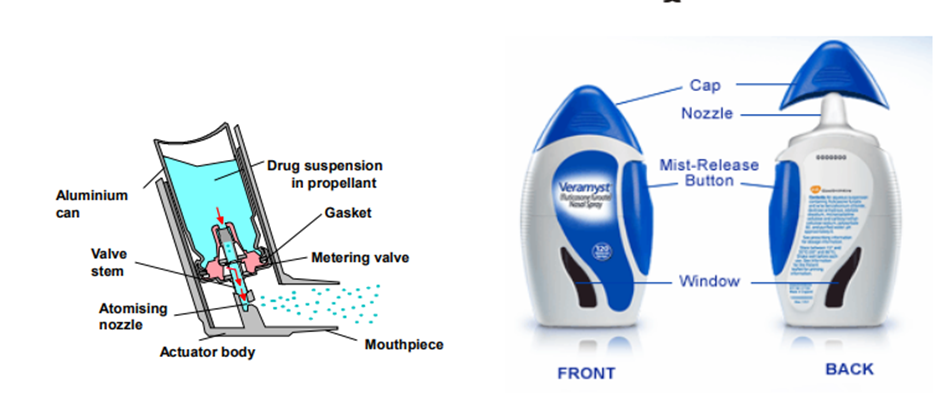
INHALER:
- Inhalers are solutions, suspensions or emulsion of drugs in a mixture of inert propellants held under pressure in an aerosol dispenser.
- Release of a dose of the medicament in the form of droplets of 50 um diameter or less from the container through a spring-loaded valve incorporating a metering device. The patient then inhales the released drug through a mouthpiece.
- In some types, the valve is actuated by finger pressure, in other types the valve is actuated by the patient breathing in through the mouthpiece.
- It is commonly used to treat asthma and other respiratory problems.

OPHTHALMIC DOSAGE FORMS:
EYE DROPS:
Eye drops are saline-containing drops used as a vehicle to administer medication in the eye. Depending on the condition being treated, they may contain steroids, antihistamines or topical anesthetics. Eye drops sometimes do not have medications in them and are only lubricating and tear-replacing solutions.

OTIC DOSAGE FORMS:
EAR DROPS:
- Ear drops are solutions, suspensions or emulsions of drugs that are instilled into the ear with a dropper.
- It is used to treat or prevent ear infections, especially infections of the outer ear and ear canal.
NASAL DOSAGE FORMS:
NASAL DROPS AND SPRAYS:
Drugs in solution may be instilled into the nose from a dropper or from a plastic squeeze bottle. The drug may have a local effect, e.g. antihistamine, decongestant.
Alternatively, the drug may be absorbed through the nasal mucosa to exert a systemic effect. The use of oily nasal drops should be avoided because of possible damage to the cilia of the nasal mucosa.

Nice and very informative
Thank You